enzymatic gravimetric method explained|Implications of two different methods for analyzing total dietary fib : company The AOAC method is an enzymatic- gravimetric procedure to determine the total dietary fibre (TDF). The Englyst method involves enzymatic-chemical extraction and fractionation of the . On the first day of school, Rue has a new friend, Jules, but struggles to put the past behind her. 3. Made You Look. Kat starts camming. Jules falls for a boy online. Rue is confronted at NA, and Cassie visits McKay at college. 4. Shook Ones Pt. 2. Rue, trying to get clean for Jules, chaperones Gia at the carnival.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 9 de mai. de 2022 · La espera ha terminado. Regresa al increíble mundo de Pandora con #Avatar #ElSentidoDelAgua.
Enzymes employed had to meet specific activity requirements and be devoid of contaminating enzymes active on dietary fibre components. The method that evolved was AOAC Official Method 985.29 ‘Total Dietary Fiber in .The AOAC method is an enzymatic- gravimetric procedure to determine the total dietary fibre (TDF). The Englyst method involves enzymatic-chemical extraction and fractionation of the .
This study aimed at determining the total dietary fiber contents in yacon root pulp (YRP) and yacon flour (YF) by the AOAC enzymatic .Enzymatic-gravimetric methods. In the early 1980s, a enzymatic-gravimetric method was developed in which the sum of soluble and insoluble polysaccharides and lignin were . Since 1989, total dietary fiber values in USDA databases were determined by the enzymatic-gravimetric (EGF) method (AOAC 991.43), where “fiber” is the residue remaining .This chapter discusses the commonly used analytical methods for protein, fat and carbohydrate, and makes recommendations regarding the preferred methods for the current state of the art and available technology.
Implications of two different methods for analyzing total dietary fib
Implications of two different methods for analyzing total dietary
Enzymatic methods for determining sugar content rely on the ability of an enzyme to catalyze a specific reaction and employ a suitable method for monitoring the progression of the reaction or.
Enzymatic gravimetric methods date back to the 19th century. In the 1930s, McCance et al. measured total unavailable carbohydrates in fruits, nuts, and vegetables by determining the . Method AOAC 2011.25 (McCleary, 2010) is an enzymatic–gravimetric method combined with liquid chromatography. Samples were digested by α-amylase, .
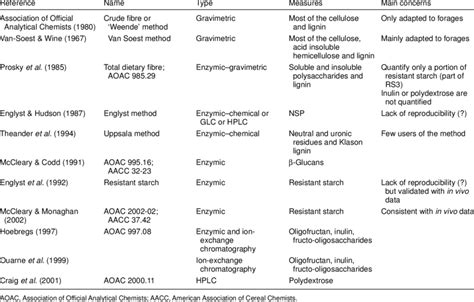
Dietary fibre in foods: a review
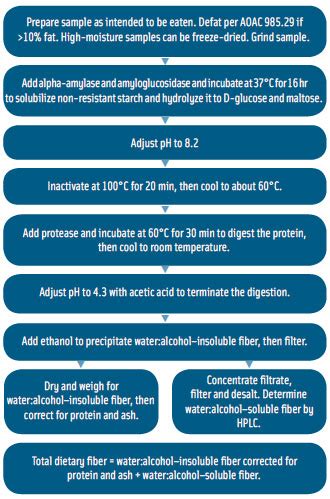
DOI: 10.1093/JAOAC/75.3.395 Corpus ID: 128658872; Determination of total, soluble, and insoluble dietary fiber in foods: enzymatic-gravimetric method, MES-TRIS buffer: collaborative study Abstract. A method for the determination of total dietary fiber (TDF), as defined by the CODEX Alimentarius, was validated in foods. Based upon the principles of AOAC Official Methods SM 985.29, 991.43, 2001.03, and 2002.02, the method quantitates high- and low-molecular-weight dietary fiber (HMWDF and LMWDF, respectively). In 2007, McCleary . The method that evolved was AOAC Official Method 985.29 ‘Total Dietary Fiber in Foods; Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method’ 4, 5. Subsequently, the method was extended to allow measurement of total, soluble and insoluble .AOAC OFFICIAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS Supplement March 1995 32.1.17 AOAC Official Method 991.43 Total, Soluble, and Insoluble Dietary Fiber in Foods Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method, MES—TRIS Buffer First Action 1991 Final Action 1994 (Applicable to processed foods, grain and cereal products, fruits, and vegetables.) Method Performance:
Dietary Fibre and Resistant Starch Analysis
Enzymatic gravimetric methods date back to the 19th century. In the 1930s, McCance et al. measured total unavailable carbohydrates in fruits, nuts, and vegetables by determining the residue . As for enzymatic-gravimetric method, above, but including non-digestible carbohydrates with three or more monomeric units (intrinsic and added components). . (Raatz et al., 2016) could explain these results, given that the EGF analysis likely made the potato starch accessible to the digestive enzymes during the autoclaving step that is part . This method extends the capabilities of the previously adopted AOAC Official Method 2009.01, Total Dietary Fiber in Foods, Enzymatic–Gravimetric– Liquid Chromatographic Method, applicable to plant material, foods, and food ingredients consistent with CODEX Definition 2009, including naturally occurring, isolated, modified, and synthetic . Because the release of a volatile species is an essential part of these methods, we classify them collectively as volatilization gravimetric methods of analysis. 8.4: Particulate Gravimetry Precipitation and volatilization gravimetric methods require that the analyte, or some other species in the sample, participates in a chemical reaction.
Enzymatic gravimetric methods date back to the 19th century. In the 1930s, McCance et al. measured total unavailable carbohydrates in fruits, nuts, and vegetables by determining the residue insoluble in 80% ethanol. This was corrected for starch measured after enzymatic hydrolysis with taka-diastase and for protein. Method AOAC 2011.25 (McCleary, 2010) is an enzymatic–gravimetric method combined with liquid chromatography. Samples were digested by α-amylase, amyloglucosidase and protease (K-INTDF; Megazyme, Ireland). Before the filtration, . [orange] to +255.9 % [mandarin]). Differences in determined IDF values between used methods are hard to explain . OMA 2022.01 is a robust and reproducible method for the analysis of insoluble, soluble (SDFP and SDFS), and TDF in a wide range of matrixes. . Soluble, and Total Dietary Fiber in Foods Using a Rapid Integrated Procedure of Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatography: First Action 2022.01 J AOAC Int. 2022 Dec 22;106(1):127-145. doi: 10.1093 .
What is Gravimetric Analysis? Gravimetric analysis is a method in analytical chemistry to determine the quantity of an analyte based on the mass of a solid. Example: Measuring the solids suspended in the water sample – Once a known volume of water is filtered, the collected solids are weighed. The principle of Gravimetric Analysis:Two methods (an AOAC and a simplified enzymatic-gravimetric method) were used to analyze seven types of canned legumes and eight cooked legumes. Total dietary fiber (TDF) of the canned products ranged between 17% and 23% (dry basis) for chick peas, . This may explain why the starch in canned beans could be readily hydrolyzed even under .
Development and Evolution of Methods Used to Extract and Measure Dietary Fiber
Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method and Liquid Chromatography Determination First Action 2001 [This method is applicable to resistant maltodextrin (RMD) and to foods containing RMD listed in Table 2001. .

refractometer specific gravity urine principle
The dietary fibre content in white wheat bread, measured with an enzymatic, gravimetric method, was almost 20% higher than in the corresponding flour. . The increment was largely explained by .A collaborative study was conducted to determine the total dietary fiber (TDF) content of food and food products, using a combination of enzymatic and gravimetric procedures. The method was basically the same as published earlier (J. Assoc. Off. Anal. Chem. (1984) 67, 1044-1052), with changes in the .
Most gravimetric methods for total dietary fiber (TDF) determination require the complete removal of starch and the partial removal of protein wi . dilute alcohol extractions of a few selected fruits and vegetables gave residue weights comparable to those after enzymatic treatments. We were able to show later that simply suspending the .
refractometer specific gravity validation
Enzymatic-Gravimetric Method and Liquid Chromatography: Collaborative Study BARRY V. M CCLEARY Megazyme International, Bray Business Park, Bray, Co. Wicklow, Ireland JONATHAN W. D EVRIES Method 925.10 in Official Methods of Analysis, 18th Edition (AOAC International, 2007) provides an approved method for determining the moisture content of flour. A preweighed sample is heated for one hour in a 130 o C oven and transferred to a desiccator while it cools to room temperature. Enzymatic–gravimetric methods have been recommended to determine dietary fiber. Recently in Brazil, the method 985.29 of AOAC (1990) was adopted for fiber levels notification on the label of packed food products (Brasil, 1998).Several problems as to the performance of these modifications of the method have been recorded (Jeraci and Van Soest, .
AOAC Official Method AOAC 985.29-1986(2003), Total dietary fiber in foods. Enzymatic- - The files are in electronic format(PDF/DOC/DOCX) and will be sent to your email within 24 hours. Test Method:AOAC 985.29-1986(2003)Title:Total dietary fiber in foods. Enzymatic-gravimetric methodPages:2
Methodology to support this definition was separately developed by Furda (8, 9), Schweizer and Wursch (10, 11), and Asp and Johansson , leading to the enzymatic gravimetric Official Method of Analysis SM (OMA) for total DF (TDF) [Prosky et al. ; OMA 985.29] as well as for insoluble DF (IDF) and soluble DF that precipitates in 78% aqueous .Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatography First Action 2011 [Applicable to plant material, foods, and food ingredients . method combines the key attributes of AOAC Official Methods of AnalysisSM 985.29 (and its extensions, 991.42 and 993.19), 991.43, 2001.03, and 2002.02. Duplicate test portions are incubated withThis method extends the capabilities of the previously adopted AOAC Official Method 2009.01, Total Dietary Fiber in Foods, Enzymatic-Gravimetric-Liquid Chromatographic Method, applicable to plant material, foods, and food ingredients consistent with CODEX Definition 2009, including naturally occurring, isolated, modified, and synthetic polymers . A simplified enzymatic-gravimetric method for total dietary fiber (TDF) determination has been published and used in the Food Composition Laboratory of the U.S. Department of Agriculture since 1988. This method gives comparable results to AOAC Official Methods 985.29 and 991.43 but the AOAC methods use 100°C (water bath) to gelatinize the .
The original AOAC enzymatic-gravimetric method for the determination of total dietary fibre (TDF) was developed on basis of the joint experience of Asp et al. (1992). The origins of these methods can be tracked back to the biochemical approach of measuring the indigestible residues in human foods introduced by In 1985 the Association of Official Analytical Chemists (AOAC) adopted an enzymatic-gravimetric method, in which samples are subjected to serial digestion with amylase, amyloglucosidase, and protease, followed by isolation and gravimetric measurement of the residue as fiber (EGF). This method was first accepted in 1994 by the U.S. Food and Drug .
refractometer sper scientific
refractometer stage
Para acessar os resultados e laudos de exames, clique nos links abaixo. Exames laboratoriais. (por exemplo, testes para diagnóstico do coronavírus (COVID-19); exames .
enzymatic gravimetric method explained|Implications of two different methods for analyzing total dietary fib